Microsystems for integrated optics
Optical micro systems described previously can be considered free-space optical systems as the mobile structures (mirrors, gratings, etc.) interact with light during its spread in the air. On the contrary, in integrated optics, light is contained in waveguides carried out on the appropriate optical materials, such in the picture below.
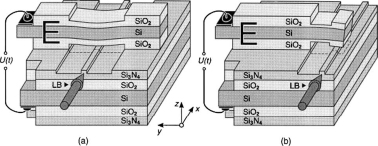
In this case, it's obviously hard to control the propagation of light with mirrors or diffraction gratings upon direct contact with the light beam. However, there are other means to control light, with mechanical structures in integrated optics. They are based on the coupling by evanescent waves between guided light and dielectric structures such as bridge or beam gantry, suspended on waveguides. Basically these devices are phase modulators and work by modifying the guides refractive index, modifying so the light group speed.
For instance, we can make a 2 x 2 optical switch on the basis of a Mach-Zehnder interferometer in which the phase delay is controlled by a micro system using the phase modulation.