| coustique |
|
"DEFINITION" OF
MECHANICS
source : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mechanics
|
 |
Mechanics is the original discipline of physics, dealing with the macroscopic world that humans perceive. It is therefore a huge body of knowledge about the natural world. Mechanics encompasses the movement of all matter in the universe under the four fundamental interactions (or forces): gravity, the strong and weak interactions, and the electromagnetic interaction.
Mechanics also constitutes a central part of technology,
the application of physical knowledge for humanly defined purposes. In
this connection, the discipline is often known as engineering or applied mechanics. In this sense,
mechanics is used to design and analyze the behavior of structures,
mechanisms,
and machines.
Important aspects of the fields of mechanical engineering,
aerospace engineering,
civil engineering, structural engineering,
materials engineering,
biomedical engineering
and biomechanics
were spawned from the study of mechanics.
The following are described as forming Classical mechanics:
 |
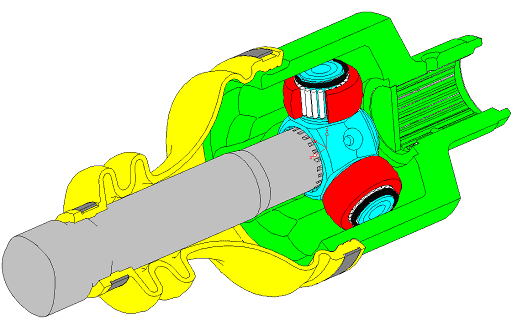 |
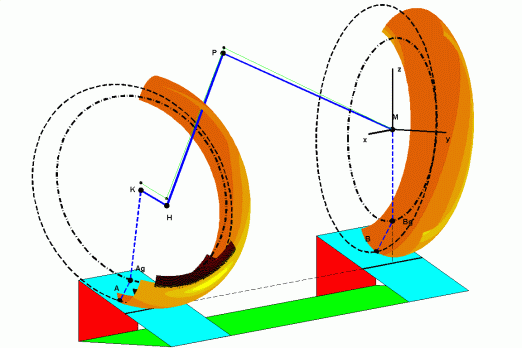
| Two-wheeled single track vehicle. Taking into account roll and steering angles , the mechanical model starts with the calculation of the ground contact point A and B, respectively for front and rear wheel. The toric geometry and the rigid behaviour of the wheels are assumed. In particular, the variation of the pitch angle due to the steering is illustrated by the difference between the blue line KHPM and the green line. . | Automotive transmission joint close to the gearbox. The drawing shows the tulip (in green) driven by the gearbox shaft, the tripod (in blue) transmitting the torque to the intermediate shaft and the trunnions in red. In real configuration where the joint angle is close to several degrees , this mechanical system behaves as a shudder vibration generator. |