Introduction
To understand this case study, prerequisites in geometrical optics and photometric are needed.
____________________________________________________________________
This case study tackles the choice of an image sensor to image a patch of agarose gel with immobilized luminescent bacteria. The patches are small squares with a surface of \(\Delta A_{S} =5\times 5\text{ mm}^{2}\). The type of sensor used will be CCD, with an objective whose focal length is \(f'=18\text{ mm}\), whose transmission is \(T_{opt}=0.9\) and whose apertures are \(N= \{ 2.8 ;4 ;5.6 ;8 ;11.3 ;16 ;22.6 ;32}\).
The bacteria's luminescence is wide band around \(\lambda =500\), but the wavelength peak will be taken into account for these measurements. The luminance was measured by spectrophotometry to be \(L_{0}=1\times 10^{-4}\text{ W.sr}^{-1}\text{.m}^{-2}\).
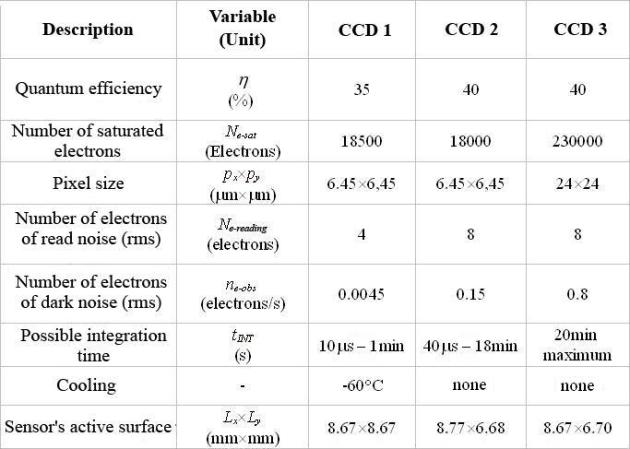
There are three sensors to chose from. Their technical data, coming from the manufacturing data, are indicated in table 1.