
Animations
 |
Animations |
 |
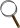
 |
The interaction of
an oblique plane wave with an interface separating two fluid media
causes a reflected
wave in the medium 1 and a transmitted
wave in the medium 2.
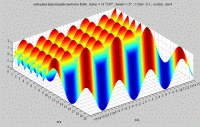
The whole field in the medium 1, which is the summation of the incident and reflected fields, has always a stationary character in the direction perpendicular to the interface (following y), and a propagative character in the direction of the interface dans la direction de l'interface (following x). 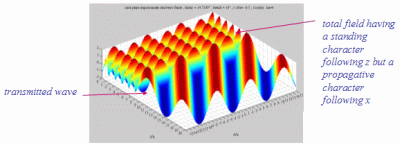 |
|
When the
propagation velocities c1 and c2
of the waves in media 1 and 2 are such that c1
< c2, there exists a value for the
incident angle
 1,
denoted 1,
denoted  c, and called critical
angle for the given interface, such that sin c, and called critical
angle for the given interface, such that sin  c = c1/c2,
from which the transmitted wave in the medium 2 becomes evanescent.
The modulus of the reflection coefficient in the medium 1 thus becomes
equal to 1 (total
reflection), but there is still presence of acoustic
energy in the medium 2. c = c1/c2,
from which the transmitted wave in the medium 2 becomes evanescent.
The modulus of the reflection coefficient in the medium 1 thus becomes
equal to 1 (total
reflection), but there is still presence of acoustic
energy in the medium 2.The evanescent
transmitted wave
propagates in a direction parallel to the interface, while its
amplitude has an exponential decreasing with the depth (when y
increases), in a direction perpendicular to the interface.
|
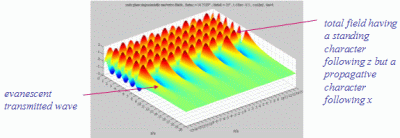 |
| The
cartographies below represent the amplitude of the real part of the
acoustic pressure; color level (red = maximum, blue = minimum). The oblique black lines represent incident, reflected and transmitted rays, as they are predicted by Snell-Descartes' laws: when the transmitted wave is propagative (  < < c),
it propagates in the direction of its transmitted ray, this direction
being perpendicular to the wave planes. c),
it propagates in the direction of its transmitted ray, this direction
being perpendicular to the wave planes. |
|
|
Incident angle inferior to the
critical angle
 c . c .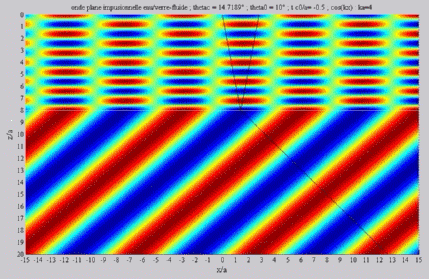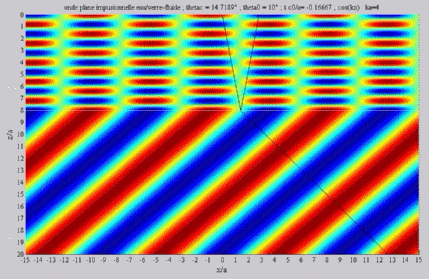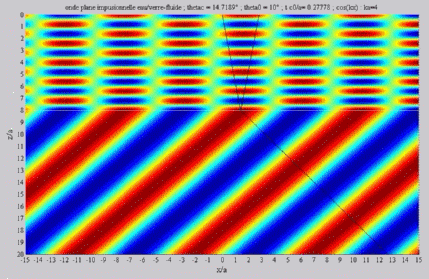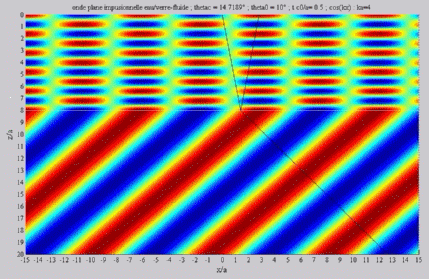 |
Incident angle superior to the
critical
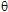 c . c .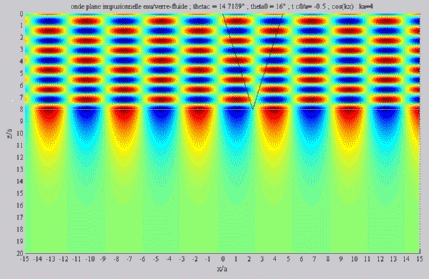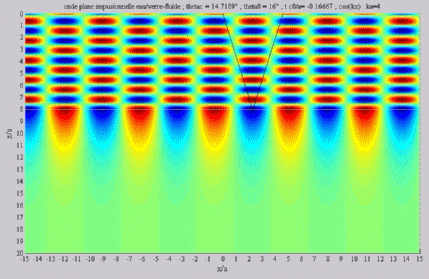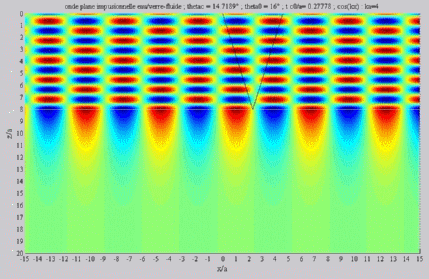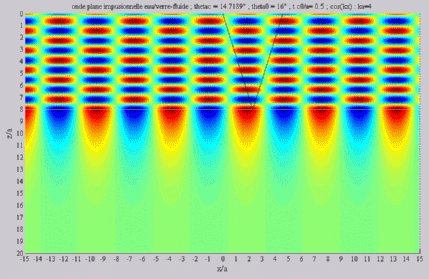 |
|
Incident angle equal to the
critical angle
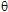 c . c .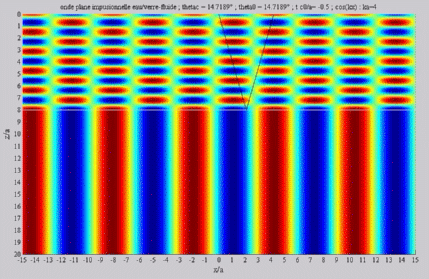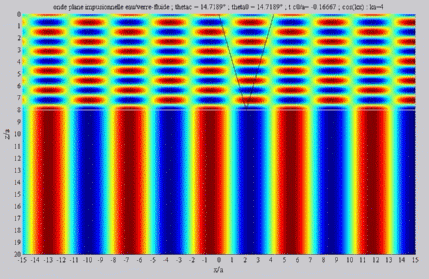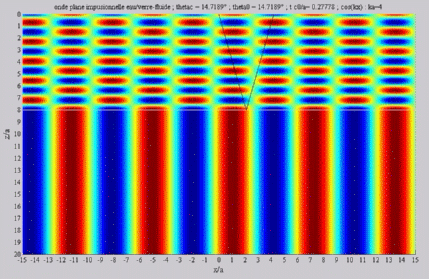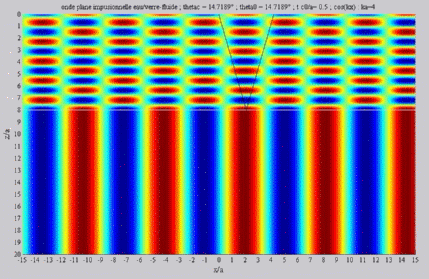 |
|